User Defined Commands
User Defined Commands enable you to create custom automation commands that integrate seamlessly into Multi Commander's interface through menu bars, button panels, keyboard shortcuts, and command line access. This powerful feature transforms Multi Commander into a personalized file management environment that automates repetitive tasks, launches external applications, and executes complex operations with a single action.
Command Automation System
Create sophisticated automation commands using five distinct command types - from simple internal commands to advanced MultiScript programs. These custom commands integrate into Multi Commander's interface exactly like built-in features, providing unlimited extensibility for your specific workflow requirements and file management tasks.
User Defined Commands Overview
User Defined Commands extend Multi Commander's functionality by allowing you to create custom commands that automate complex operations, integrate external applications, and streamline repetitive tasks through a unified command system.
Access and Integration
User Defined Commands appear seamlessly in Multi Commander's menu system alongside built-in features
Command Integration Points
- Menu Bar: Add commands to any menu in the main menu bar
- Button Panel: Assign commands to toolbar buttons for one-click access
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Create custom hotkey combinations for instant command execution
- Command Line: Execute commands directly from the command line bar
- Context Menus: Add commands to right-click context menus
- User Menus: Create custom menu categories for organized command access
- Quick Launch: Access through the quick launch bar system
- Alias System: Create memorable aliases for complex command IDs
Command Capabilities
- File Operations: Automate copying, moving, renaming, and organizing files
- External Applications: Launch programs with specific parameters and file inputs
- System Integration: Execute batch scripts and system commands
- Advanced Scripting: Create sophisticated automation using MultiScript language
Command Configuration
Access the User Defined Commands Editor
Navigate to Configuration → User Defined Commands to open the command management interface.
Basic Command Properties
- Command Name: Descriptive name for identification and menu display
- Tooltip/Description: Detailed description shown in tooltips and help
- Command Type: Select from five available command types
- Unique ID: Auto-generated identifier for command line access
Command Organization
- Categories: Group related commands for better organization
- Naming Conventions: Use descriptive names that indicate function
- Version Control: Export and import commands for backup and sharing
Getting Started with User Defined Commands
Creating your first User Defined Command involves a straightforward process of defining the command properties, selecting the appropriate command type, and assigning it to an interface element for easy access.
Step-by-Step Command Creation
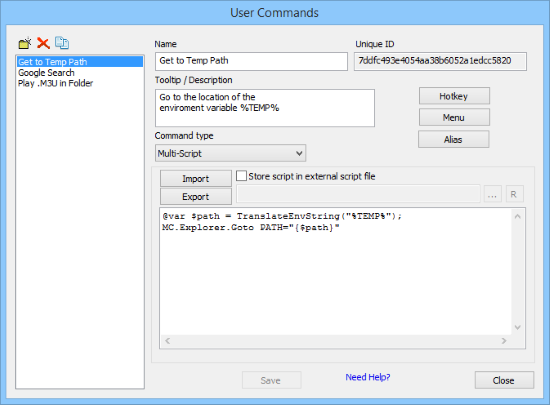
The User Defined Commands dialog provides a comprehensive interface for creating and managing custom commands
Command Creation Process
- Open the Editor: Access Configuration → User Defined Commands from the menu bar
- Create New Command: Click the New button and enter a descriptive command name
- Add Description: Fill in the tooltip/description field for user guidance and menu display
- Select Command Type: Choose from the five available command types based on your requirements
- Configure Command: Set up the specific parameters and options for your chosen command type
- Save Command: Press the Save button to store your command configuration
- Assign Access Method: Configure buttons, hotkeys, menu items, or aliases for command access
Command Naming Best Practice
Use clear, descriptive names that indicate the command's function. Good examples: "Backup Documents to USB", "Open Current Folder in VS Code", "Convert Images to JPEG".
Command Type Reference
Multi Commander provides five distinct command types, each designed for specific automation scenarios and offering different levels of complexity and functionality.
Complete Command Type Overview
| Command Type | Description | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Commands | Execute existing Multi Commander functions and extension commands | Quick access to built-in features, menu shortcuts, extension functions |
| External Commands | Launch external applications and system programs | Opening files with specific applications, launching utilities, system tools |
| Batch Script (.BAT) | Execute Windows batch scripts with dynamic tag support | System administration, file processing, multi-step operations |
| Custom Commands | Simple command syntax for Multi Commander operations | File operations, view changes, panel manipulation, basic automation |
| MultiScript | Advanced scripting language with full programming capabilities | Complex automation, conditional logic, advanced file processing |
Simple Command Types
Internal Commands
- Purpose: Access existing Multi Commander functions
- Setup: Select module and specific command from dropdowns
- Benefits: No scripting required, immediate access to all features
- Examples: View file, copy files, change panel view
External Commands
- Purpose: Launch external programs and applications
- Setup: Specify program path and command line parameters
- Benefits: Integrate any Windows application with Multi Commander
- Examples: Open with Notepad++, launch Git client, run system utilities
Advanced Command Types
Custom Commands
- Purpose: Simple syntax for Multi Commander operations
- Setup: Use helper functions and parameter lists
- Benefits: Easy to learn, powerful file management capabilities
- Examples: Select files by pattern, change view filters, navigate paths
Batch Scripts or MultiScript
- Purpose: Advanced automation and complex operations
- Setup: Write scripts with variables, conditions, and loops
- Benefits: Unlimited flexibility, sophisticated automation
- Examples: Batch file processing, conditional operations, system integration
Command Assignment Methods
Once created, User Defined Commands must be assigned to interface elements to provide easy access. Multi Commander offers multiple assignment methods to integrate commands into your preferred workflow.
Interface Integration
Button Panel Assignment
- Access: Use the Button Editor to configure toolbar buttons
- Setup: Select "User Defined Command" type and choose your command
- Benefits: One-click access, visual command representation
- Features: Tooltip display, icon customization, button grouping
Menu Integration
- Access: Use the Menu button in the command editor
- Setup: Add commands to existing or custom menu categories
- Benefits: Organized command access, hierarchical structure
- Features: Sub-menus, separators, keyboard accelerators
Direct Access Methods
Keyboard Shortcuts
- Access: Use the HotKey button to open Keyboard Customization
- Setup: Assign key combinations to commands
- Benefits: Fastest access method, muscle memory development
- Features: Modifier keys (Ctrl, Alt, Shift), function keys, custom combinations
Command Line Access
- Access: Use the unique command ID in the command line bar
- Setup: Create aliases using the Alias Editor
- Benefits: Scriptable access, memorable command names
- Features: Parameter passing, command chaining, automation integration
Assignment Workflow Guide
Recommended Assignment Process
- Determine Usage Frequency: Assign frequently used commands to buttons or hotkeys
- Consider Command Context: Place file-specific commands in context menus
- Group Related Commands: Organize similar commands in custom menus or button groups
- Create Memorable Aliases: Use descriptive aliases for command line access
- Test Integration: Verify command access works as expected in your workflow
Best Practices for Command Access
- Consistent Placement: Keep related commands in predictable locations
- Logical Grouping: Group commands by function or file type
- Clear Naming: Use descriptive names that indicate command purpose
- Avoid Conflicts: Check for existing hotkey assignments before creating new ones
- Document Commands: Maintain notes about complex command configurations
- Regular Review: Periodically review and optimize command assignments
- Backup Configuration: Export command definitions for backup and sharing
- User Training: Document custom commands for team environments
User Defined Commands Mastery
Master User Defined Commands by starting with simple Internal and External commands before progressing to Custom Commands and advanced scripting. Remember that effective command organization through clear naming, detailed descriptions, and logical assignment methods creates a powerful automation environment. Use the unique command ID system with aliases for command line access, leverage the Button Editor and Menu Editor for interface integration, and maintain your command library through regular testing, documentation, and cleanup for sustained productivity improvements.
Related Command Documentation
Explore specific command types and integration methods: Internal Commands, External Commands, Custom Commands, Batch Scripts, MultiScript, Button Editor, Keyboard Customization, and Alias Editor.