User Defined Commands - Internal Commands
Internal Commands represent the simplest and most direct way to create User Defined Commands by leveraging Multi Commander's existing functionality. These commands provide immediate access to built-in features, extension functions, and plug-in capabilities through a unified command interface, making them ideal for creating shortcuts, aliases, and custom menu entries for frequently used operations.
Built-in Function Access
Internal Commands directly execute existing Multi Commander functions, extension commands, and plug-in operations without requiring any scripting or complex configuration. Simply select the desired function from organized dropdown menus to create instant access to any built-in capability through buttons, hotkeys, menus, or command line aliases.
Internal Commands Overview
Internal Commands provide direct access to Multi Commander's extensive built-in functionality, including core file operations, view management, navigation commands, and all features provided by installed extensions and plug-ins.
What Are Internal Commands?
Command Types Available
- Core Functions: File operations, navigation, view management
- Menu Commands: All menu bar and context menu functions
- Toolbar Functions: Button panel operations and tool commands
- Panel Operations: Explorer panel manipulation and configuration
- Extension Commands: Functions provided by installed extensions
- Plug-in Functions: Operations from loaded plug-in modules
- System Integration: Windows shell integration commands
- Advanced Features: Specialized tools and utilities
Key Characteristics
- No Scripting Required: Simple selection from organized dropdown menus
- Immediate Execution: Commands run instantly when triggered
- No Parameters: Functions execute with their default behavior
- Full Integration: Access to every built-in Multi Commander capability
Simplicity Advantage
Internal Commands offer the fastest path from idea to implementation - no scripting knowledge required, just select the function you want to access and save the command.
Benefits of Internal Commands
Immediate Access
- Quick Setup: Create commands in seconds without scripting
- Reliable Execution: Commands use tested, built-in functionality
- Consistent Behavior: Functions behave exactly like menu or toolbar access
- No Maintenance: Commands automatically stay current with software updates
Interface Customization
- Personal Shortcuts: Create hotkeys for any menu function
- Custom Buttons: Add frequently used functions to button panels
- Menu Organization: Group related functions in custom menus
- Command Line Access: Create memorable aliases for complex function names
Primary Use Cases
Workflow Optimization
- Frequently Used Functions: Quick access to operations you use daily
- Hidden Menu Items: Surface functions that aren't prominently displayed
- Extension Features: Easy access to powerful extension capabilities
- Efficiency Improvements: Reduce clicks and navigation time
Interface Personalization
- Preferred Access Methods: Use buttons instead of menus or vice versa
- Logical Grouping: Organize functions by your workflow patterns
- Memorable Names: Create command line aliases you can easily remember
- Consistent Interface: Standardize access across different Multi Commander installations
Configuring Internal Commands
Setting up Internal Commands involves a straightforward two-step selection process that provides access to every available function in Multi Commander and its installed extensions.
Configuration Interface
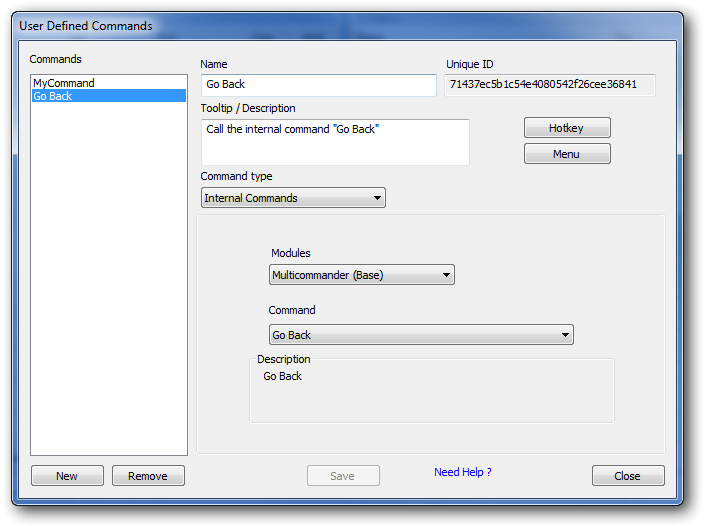
The Internal Commands configuration interface showing the two-dropdown selection system
Configuration Process
- Select Command Type: Choose "Internal Commands" when creating your User Defined Command
- Choose Module: Select the module containing your desired function from the first dropdown
- Select Function: Choose the specific command from the second dropdown
- Save Command: Complete the command creation process
- Assign Access: Configure buttons, hotkeys, menus, or aliases for the command
Two-Dropdown System
First Dropdown: Module Selection
- Core Modules: Multi Commander's built-in functionality
- Extension Modules: Installed extension packages
- Plug-in Modules: Loaded plug-in components
- System Modules: Windows integration functions
Second Dropdown: Function Selection
- Dynamic Content: Updates based on first dropdown selection
- Organized Functions: Commands grouped by functional area
- Descriptive Names: Clear function descriptions for easy identification
- Complete Access: Every available function in the selected module
Module Categories
Core Multi Commander Modules
- File Operations: Copy, move, delete, rename functions
- View Management: Panel layout, view modes, sorting
- Navigation: Path changes, history, bookmarks
- Selection: File selection patterns and operations
- Search: Find functions and search operations
- Tools: Built-in utilities and system tools
Module Organization
Modules are logically organized by functionality, making it easy to find the specific command you need.
Extension & Plug-in Modules
Extension-Provided Functions
- Archive Tools: Advanced compression and extraction
- File Viewers: Specialized file viewing capabilities
- Development Tools: Programming and development utilities
- System Utilities: Advanced system management functions
- Custom Extensions: User-created or third-party extensions
Dynamic Availability
- Installation Dependent: Available modules depend on what's installed
- Automatic Detection: New extensions appear automatically in the list
- Version Updates: Module content updates with extension updates
- Organized Display: Extensions grouped separately from core functions
Common Uses for Internal Commands
Internal Commands excel in specific scenarios where you need quick, reliable access to existing functionality without the complexity of scripting or parameter configuration.
Workflow Acceleration
Creating Command Line Aliases
Transform complex menu navigation into simple command line entries:
- Quick Navigation: Create aliases like "home" for "Go to Home Directory"
- View Changes: Use "details" or "thumbs" for view mode switches
- Tool Access: Create "calc" for calculator, "search" for file search
- Function Shortcuts: Simplify access to buried menu functions
Custom Button Creation
Add frequently used functions to button panels:
- Daily Operations: File operations you perform regularly
- View Toggles: Quick switches between different panel views
- Extension Tools: One-click access to extension functions
- System Integration: Windows shell function buttons
Interface Customization
Menu Organization
Surface hidden or deeply nested functions:
- Hidden Functions: Make rarely-visible functions easily accessible
- Personal Menus: Create custom menu categories for your workflow
- Quick Access: Move frequently used items to prominent locations
- Logical Grouping: Organize functions by task rather than technical category
Keyboard Shortcut Assignment
Create hotkeys for any function:
- Muscle Memory: Assign keys that match your work patterns
- Efficiency Gains: Eliminate menu navigation for common tasks
- Consistent Access: Use the same hotkeys across different computers
- Extension Functions: Create shortcuts for powerful extension capabilities
Internal Commands Best Practices
Master Internal Commands by exploring all available modules to discover useful functions, creating meaningful aliases for command line access, and organizing frequently used functions into logical button groups or custom menus. Remember that Internal Commands provide the fastest path to functionality - when you need direct access to existing features without customization, they offer immediate, reliable execution with zero maintenance requirements. Use them as building blocks for more complex automation workflows.
Related Command Documentation
Explore other User Defined Command types: User Defined Commands Overview, External Commands, Custom Commands, Batch Scripts, MultiScript, and integration tools: Button Editor, Keyboard Customization, Alias Editor.