Language Editor and Translation System
Multi Commander's Language Editor provides a comprehensive translation and localization platform that enables the creation of new language packs and modification of existing translations with professional-grade editing capabilities. This sophisticated system supports complete internationalization workflows, offering intuitive interfaces for translators, automated language pack management, and seamless integration with Multi Commander's multilingual architecture for global accessibility.
Professional Translation and Localization Platform
Experience comprehensive translation capabilities that combine intuitive editing interfaces with advanced language pack management and automated submission systems. The Language Editor integrates seamlessly with Multi Commander's internationalization framework to provide professional translation workflows that handle multiple languages, preserve formatting and special characters, and offer complete control over localization processes for translators, language coordinators, and international distribution teams.
Language Editor Overview
The Language Editor provides comprehensive translation management capabilities that enable creation of new language packs, modification of existing translations, and professional localization workflows with advanced editing features and automated submission systems.
Language Editor Access and Capabilities
Language Editor accessible through Configuration menu for comprehensive translation management
Core Translation Features
- Language Pack Creation: Create new language support from existing templates
- Translation Editing: Modify existing translations with professional editing interface
- Text Item Management: Complete control over individual text elements and descriptions
- Special Character Support: Proper handling of control characters and formatting
- Automated Submission: Direct submission to Multi Commander development team
- Export Functionality: Generate language packs for distribution and testing
- Version Management: Backup and restore previous translation versions
- External Editor Support: Work with favorite text editors for large-scale translation
Professional Translation Support
- Extension Integration: Complete translation support for all Multi Commander extensions and plugins
- Culture Code Management: Proper language identification and automatic selection systems
- Quality Assurance: Built-in validation for translation completeness and formatting
- Collaborative Workflows: Support for team-based translation projects and partial submissions
Global Accessibility
The Language Editor empowers global communities to make Multi Commander accessible in their native languages, supporting international users and expanding the application's reach worldwide.
Language File System Architecture
Multi Commander's language system uses a sophisticated architecture that combines ZIP-based language packs with unpacked working directories, enabling efficient distribution while providing flexible development and testing capabilities for translators.
Language Pack Architecture and Loading Process
Language File Loading Sequence
1. English Base Loading
- Primary Foundation: English language pack loaded first as base template
- Complete Coverage: All text items stored in memory as fallback defaults
- Reference Standard: Provides complete text coverage for all features
- Compatibility Assurance: Ensures no missing text items regardless of translation completeness
2. Target Language Override
- Selective Replacement: Configured language overwrites translated text items
- Fallback Preservation: Untranslated items retain English defaults automatically
- Dynamic Loading: Language selection applied at runtime for immediate effect
- Quality Maintenance: Partial translations work seamlessly with English fallbacks
3. Extension Integration
- Core Integration: Built-in extensions included in main language packs
- Custom Extension Support: User extensions search for local language files
- Flexible Location: Language files found in extension directories when not in packs
- Development Support: Easy testing of custom extension translations
File System Organization
Language Pack Locations
- Installation Directory:
Languages\folder contains ZIP-based language packs - UserData Directory:
UserData\Languages\for unpacked development files - Extension Directories: Individual extension folders for custom translations
- Priority System: UserData unpacked files take precedence over ZIP archives
Development Workflow
- Pack Extraction: Language Editor unpacks ZIP files to UserData for editing
- Live Testing: Changes in UserData immediately affect application behavior
- Version Validation: System checks version compatibility before using unpacked files
- Cleanup Support: Remove UserData files to revert to ZIP-based packs
Quick Access
Type :gouserdata in the command line to navigate directly to the UserData folder for language file management.
Language Pack Structure
ZIP Archive Contents
- Naming Convention:
MC_LangPack_[code].zipformat for each language - XML Language Files: Individual files for each extension and component
- Culture Identification: Files named with culture codes (e.g.,
*_en.xml,*_fr.xml) - Complete Coverage: All Multi Commander components included in single archive
File Organization Benefits
- Distribution Efficiency: Single file contains complete language support
- Version Consistency: All components synchronized in single package
- Installation Simplicity: Drop-in language pack installation
- Backup Convenience: Easy language pack backup and sharing
Development Considerations
- Testing Flexibility: Unpacked files enable rapid testing and iteration
- Version Management: Automatic fallback when versions don't match
- Extension Support: Custom extensions work independently of main packs
- Quality Control: Staged development with production deployment
Language Editor Interface and Controls
The Language Editor interface provides comprehensive translation management through an intuitive panel system that organizes extensions, languages, and text items with professional editing capabilities and advanced management features.
Language Editor Main Interface
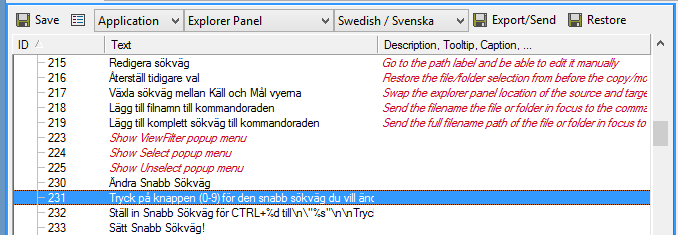
Language Editor main interface showing comprehensive translation management controls
Control Panel Overview
| Control | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Save Button | Save current language changes | Saves all modifications for the currently selected language with automatic backup |
| Language Properties | Configure language metadata | Set language name, culture code, and matching language configurations |
| Type Dropdown | Select extension category | Choose between Core, Extensions, and Plugin types for translation focus |
| Extension Dropdown | Select specific component | Lists all extensions/plugins for selected type with individual language files |
| Language Dropdown | Choose target language | Select active language for editing or add new language support |
| Export/Send Button | Generate language pack | Export completed translations or submit directly to development team |
| Restore Button | Revert to previous version | Restore from automatic backups or previous language pack versions |
Text Item Management System
Text Item List Structure
ID Column
- Format: Letter + Number combination (e.g., C-231, M-105)
- Categories: M (Menu), D (Dialog), E (Error), C (Command)
- Identification: Unique identifier for each translatable text element
- Organization: Logical grouping by functional category
Text Column
- Primary Content: Main text displayed to users
- Translation Target: The actual text requiring translation
- Format Preservation: Special characters and formatting maintained
- Context Sensitivity: Text appropriate for specific interface elements
Secondary Column
- Tooltip Text: Hover descriptions and help text
- Descriptive Content: Additional context and explanations
- Caption Support: Error message titles and dialog captions
- Extended Information: Detailed descriptions for script commands
Visual Translation Status Indicators
- Red Italic Text: Untranslated items showing English fallback text (not saved to language file)
- Bold Text: Modified items with unsaved changes requiring save operation
- Normal Text: Translated and saved items with complete localization
- Context Menu: Right-click to show only untranslated items for focused translation work
Translation Workflow Features
- Filtering Options: Show only untranslated items to focus translation efforts
- Real-Time Editing: Direct text modification with immediate visual feedback
- Progress Tracking: Visual indicators for translation completion status
- Quality Control: Automatic validation of special characters and formatting
Creating New Language Packs
The Language Editor provides comprehensive support for creating new language packs from scratch, including proper culture code configuration, language matching, and automated setup for efficient translation workflows.
New Language Creation Process
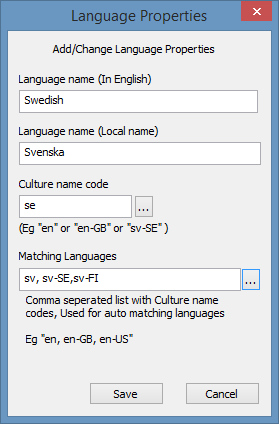
New Language Properties dialog for comprehensive language configuration
Language Creation Steps
1. Language Properties Configuration
- English Name: Language name in English for international reference
- Native Name: Language name in the target language for local users
- Culture Code: ISO language code (2 or 5 characters) for system identification
- Matching Languages: Additional culture codes for automatic language selection
2. Culture Code Guidelines
- Two-Letter Codes: General language support (e.g., 'en', 'fr', 'de')
- Five-Letter Codes: Regional variants (e.g., 'en-US', 'en-GB', 'fr-CA')
- Conflict Avoidance: Use specific codes when multiple variants exist
- Standard Compliance: Follow ISO 639-1 and ISO 3166-1 standards
3. Automatic Language Selection
- Windows Integration: System detects user's Windows language setting
- Matching Logic: Compares against configured matching languages list
- First-Run Selection: Appropriate language automatically selected on initial startup
- User Override: Manual language selection always available in settings
4. Language Registration
- SupportedLanguages.xml: Updated automatically with new language information
- System Integration: New language appears in Multi Commander language list
- Immediate Availability: Ready for translation work after creation
- Backup Creation: Original configuration preserved for rollback if needed
Practical Example: Swedish Language Configuration
Basic Configuration:
English Name: Swedish
Native Name: Svenska
Culture Code: sv
Matching Languages:
sv, sv-SE, sv-FI
Result: Auto-selected for Swedish users in Sweden or Finland
External Editor Workflow
Manual Language File Setup
- Extract English Pack: Manually unpack
MC_LangPack_en.zip - Rename Files: Change
*_en.xmlto*_[code].xmlfor new language - Create New Pack: ZIP renamed files as
MC_LangPack_[code].zip - Clean UserData: Remove old unpacked files except
SupportedLanguages.xml - Restart Editor: Language Editor will unpack all language packs
- External Editing: Edit XML files in preferred text editor
- Export Pack: Use Language Editor export function when complete
External Editing Benefits
- Familiar Tools: Use preferred text editors with advanced features
- Batch Operations: Search and replace across multiple files
- Version Control: Integrate with Git or other VCS systems
- Team Collaboration: Share files for collaborative translation projects
XML Editing Precautions
Critical XML Considerations
- UTF-8 Encoding: Maintain UTF-8 encoding for international character support
- XML Tag Preservation: Never remove or modify XML structural tags
- Special Character Encoding: Properly encode &, <, >, and quote characters
- File Validation: Test XML files in web browser to check for errors
Common XML Encoding Rules
Character Replacements:
& becomes &
< becomes <
> becomes >
" becomes "
Error Prevention and Recovery
- Backup Strategy: Keep original files before making changes
- Incremental Testing: Test files frequently during translation process
- Browser Validation: Use web browser XML validation for error detection
- Error Location: Browser reports specific line numbers for XML errors
Translation Guidelines and Special Characters
Professional translation requires understanding of special formatting characters, control sequences, and interface-specific considerations that ensure translated text functions correctly within Multi Commander's interface elements.
Control Characters and Formatting
Essential Control Characters
\n - Line Break:
Correct: "Line1\nLine2"
Incorrect: "Line1 \n Line2" (extra spaces)
Used in message boxes and multi-line text displays
Variable Placeholders
%s - String Variable:
Example: "Opening %s file"
%d - Number Variable:
Example: "%d files selected"
Variables replaced with actual values at runtime
Complex Variable Example
Text ID L-31:
%s/%s in %d/%d Files and %d/%d Folders selected
All %s and %d placeholders must be preserved in translation
Formatting Best Practices
- Exact Preservation: Keep all control characters in exact positions
- Space Management: No extra spaces before or after control characters
- Testing Importance: Verify formatted text displays correctly
- Context Understanding: Consider how variables will be displayed
Keyboard Shortcuts and Menu Accelerators
Ampersand (&) Usage for Shortcuts
Menu Shortcut Creation:
&View → View (Alt+V)
Vie&w → View (Alt+W)
Ampersand underlines following character for keyboard access
Shortcut Conflict Management
- Unique Assignment: Each menu should have unique shortcut letters
- Conflict Resolution: Move ampersand to different character when conflicts occur
- Priority System: First occurrence takes precedence in case of duplicates
- User Experience: Choose intuitive letters for keyboard navigation
Shortcut Selection Strategy
- First Letter Priority: Use first letter when possible for intuitive access
- Memorable Characters: Select prominent or distinctive letters
- Language Adaptation: Adjust shortcuts for target language word patterns
- Consistency Maintenance: Keep similar shortcuts across related menu items
Windows Standard Behavior
- Alt Key Activation: Alt reveals underlined shortcut characters
- Hierarchical Navigation: Menu bar shortcuts lead to submenu shortcuts
- Visual Feedback: Underlined characters guide keyboard navigation
- Cross-Application Consistency: Standard Windows keyboard navigation patterns
Language Pack Submission and Export
The Language Editor provides multiple export and submission options for completed translations, including direct submission to the development team and public distribution formats for sharing with the community.
Export and Submission Options
Available Export Formats
| Export Type | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Format (Email Submission) | Development team submission | Creates internal format for email submission to Multi Commander developers |
| Internal Format (HTTP Submission) | Automated submission system | Direct web service submission with submit key for automatic inclusion |
| Public Language Pack Format | Community distribution | Standard format for sharing with other users and testing on different machines |
HTTP Submission System (Recommended)
- Automated Process: Direct submission to Multi Commander web service
- Submit Key Required: Contact Multi Commander staff for submission credentials
- Quality Control: Prevents unauthorized or incorrect language pack submissions
- Automatic Integration: Approved translations automatically included in next release
- Frequent Updates: Submit changes as often as needed with valid key
- Version Control: System tracks submission history and versions
- Instant Feedback: Immediate confirmation of successful submission
- Professional Workflow: Streamlined process for serious translation contributors
Collaborative Translation Support
Partial Translation Submissions
- Incremental Progress: Submit incomplete translations for community continuation
- Team Collaboration: Multiple translators can work on same language pack
- Quality Improvement: Partial translation better than no translation at all
- Community Building: Encourage collaborative translation projects
Translation Project Management
- Progress Tracking: Visual indicators show translation completion status
- Priority Focus: Filter untranslated items to focus effort efficiently
- Version Backup: Automatic backup system preserves translation progress
- Restoration Options: Restore previous versions if needed
Community Contributions
- Open Participation: Anyone can contribute to translation efforts
- Knowledge Sharing: Share language packs with community members
- Global Impact: Enable Multi Commander access for international users
- Cultural Adaptation: Ensure appropriate cultural context in translations
Quality Assurance and Testing
Pre-Submission Validation
- Format Verification: Ensure all special characters and variables preserved
- XML Validation: Verify XML structure integrity before export
- Character Encoding: Confirm UTF-8 encoding maintains international characters
- Completeness Check: Review translation coverage and missing items
Testing Methodology
- Live Testing: Use unpacked files in UserData for real-time testing
- Interface Review: Verify translations display correctly in actual interface
- Shortcut Testing: Confirm keyboard shortcuts work without conflicts
- Context Validation: Ensure translations appropriate for interface context
Distribution Preparation
- Public Format Export: Generate standard language pack for community sharing
- Installation Testing: Verify language pack works on clean installations
- Documentation: Include translation notes and contributor information
- Version Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with target Multi Commander version
Language Editor Mastery
Master the Language Editor by understanding the ZIP-based language pack architecture with UserData unpacking for development, utilizing the comprehensive interface for systematic translation with proper control character preservation, and leveraging automated submission systems for professional translation workflows. Remember that partial translations are valuable contributions to the community, special characters like \n, %s, %d, and & must be preserved exactly, and the HTTP submission system with submit keys provides the most efficient path for contributing translations to Multi Commander. Focus on creating consistent, culturally appropriate translations that maintain interface functionality while providing natural language experience for target users.
Related Internationalization and Configuration Documentation
Enhance your translation and localization workflows with related Multi Commander features: Configuration Management, Custom Configuration Paths, Backup and Restore Configuration, Extensions and Plugins, and User Defined Commands.