Virtual Filesystem - Network Discovery (NET:)
Multi Commander's Network Virtual Filesystem (NET:) provides comprehensive network discovery and remote system access capabilities, enabling seamless integration with local network resources, shared storage, and remote desktop environments. This powerful system transforms network navigation from complex UNC path management into an intuitive browsing experience.
Intelligent Network Integration
The Network filesystem automatically discovers and catalogs network-attached devices, computers, and shared resources, presenting them in a unified interface that simplifies access to distributed file systems and remote storage.
Network Filesystem Architecture
The NET: virtual filesystem provides a sophisticated layer for network resource discovery and access, bridging the gap between local file management and distributed network storage through automated discovery and intelligent caching mechanisms.
Network Capabilities
- Automatic Discovery: Scan and identify network-attached devices
- SMB/CIFS Support: Access Windows shares and Samba resources
- Workgroup Integration: Browse workgroup and domain computers
- Service Detection: Identify file sharing services automatically
- Persistent Cache: Remember discovered devices between sessions
- Real-time Updates: Dynamic addition and removal of network resources
Access and Security
- Credential Management: Integrated Windows authentication
- Domain Integration: Seamless domain user authentication
- Guest Access: Handle anonymous network resources
- Security Context: Respect network security policies
- Connection Pooling: Efficient management of network connections
- Timeout Handling: Graceful handling of network unavailability
Network Discovery and Scanning
Multi Commander's network discovery engine provides comprehensive scanning capabilities to automatically identify and catalog network resources, making them easily accessible through the familiar file management interface.
Discovery Process
Initiating Network Scan
The network discovery process can be initiated manually or automatically:
- Navigate to NET: Device: Open the Network virtual filesystem
- Execute Scan Network Command: Trigger comprehensive network discovery
- Monitor Progress: Track scanning progress in real-time
- Review Results: Examine discovered devices and services
Network browser showing discovered computers and network-attached devices
Remote Desktop Integration (TSClient)
Multi Commander provides specialized support for Remote Desktop environments, automatically detecting and providing access to local drives when running in Terminal Services or Remote Desktop sessions.
TSClient Support
Automatic Detection
- Session Recognition: Automatically detect Remote Desktop sessions
- Local Drive Access: Access client computer drives remotely
- Drive Redirection: Support for redirected local drives
- Seamless Integration: Treat remote drives like network resources
TSClient Features
- Full File Operations: Complete read/write access to local drives
- Drag and Drop: Transfer files between local and remote systems
- Path Resolution: Automatic UNC path translation
- Performance Optimization: Efficient file transfer over RDP
Configuration Requirements
Remote Desktop Settings
- Drive Redirection: Enable local drive redirection in RDP client
- Resource Sharing: Configure appropriate resource sharing policies
- Security Policies: Ensure drive redirection is permitted
- User Permissions: Verify user has access to local drives
Network Considerations
- Bandwidth: Consider network bandwidth for file operations
- Latency: Account for network latency in file transfers
- Security: Understand security implications of drive redirection
- Compression: Leverage RDP compression for better performance
Network Device Management
Multi Commander provides comprehensive management capabilities for discovered network devices, including persistent storage, manual organization, and contextual operations through intuitive right-click menus.
Device List Management
Persistent Device Storage
The Network filesystem maintains a persistent list of discovered devices:
- Automatic Persistence: Device list remembered between Multi Commander sessions
- Cache Management: Intelligent caching balances performance and accuracy
- Stale Device Cleanup: Automatic removal of unavailable devices over time
- Manual Override: User control over device list management
Device Access
Accessing discovered network devices is straightforward:
- Double-click Device: Open device in current panel
- Enter Key: Navigate to device like entering a folder
- Drag to Panel: Open device in opposite panel
- Right-click Options: Access additional device operations
Seamless Integration
- UNC Path Translation: Automatic conversion to appropriate network paths
- Authentication Flow: Integrated Windows authentication handling
- Error Handling: Graceful handling of access issues and network problems
Device Operations
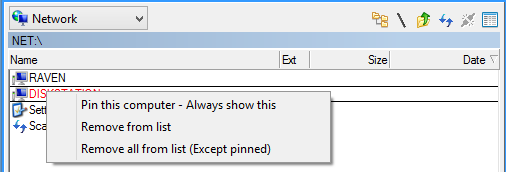
Right-click context menu showing network device management options
Available Commands
- Pin Computer: Permanently retain device in list
- Remove from List: Delete specific device entry
- Remove All (Except Pinned): Clear unpinned devices
- Refresh Device: Update device information
- Properties: View detailed device information
Network Filesystem Configuration
Multi Commander provides comprehensive configuration options for the Network filesystem, allowing fine-tuning of discovery methods, caching behavior, and performance characteristics to match specific network environments.
Configuration Interface
Accessing Settings
Network filesystem settings can be accessed through the Settings command in the NET: device interface.
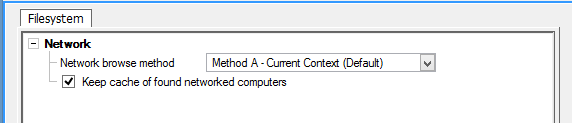
Network filesystem configuration dialog showing browse methods and caching options
Configuration Categories
- Discovery Methods: Configure how devices are discovered
- Caching Behavior: Control device list persistence
- Performance Settings: Optimize for network characteristics
- Security Options: Configure authentication and access controls
Key Settings
Network Browse Method
- Current Context: Use current user security context
- Global: Use system-wide network discovery
- Shell: Use Windows Shell network enumeration
Cache Management
- Keep Cache: Persist device list between sessions
Network Integration Features
The Network filesystem extends beyond basic device discovery, providing comprehensive integration with Multi Commander's broader file management ecosystem and enterprise networking capabilities.
System Integration
Multi Commander Integration
- Favorites System: Bookmark frequently accessed network locations
- Tab Sessions: Include network locations in saved tab sessions
- User Commands: Create custom commands for network operations
- Script Support: MultiScript functions work with network paths
Windows Integration
- Explorer Consistency: Behavior consistent with Windows Explorer
- Shell Extensions: Support for Windows Shell extensions on network resources
- Context Menus: Windows context menus available for network files
- Association Support: File associations work with network files
Enterprise Features
Domain Environment Support
- Active Directory Integration: Automatic discovery of domain resources
- Group Policy Compliance: Respect network access policies
- Kerberos Authentication: Secure authentication in domain environments
- DFS Support: Work with Distributed File System namespaces
Performance and Reliability
- Connection Pooling: Efficient management of network connections
- Offline Handling: Graceful handling of network disconnections
- Retry Logic: Automatic retry for temporary network issues
- Error Recovery: Robust error handling and recovery mechanisms
Efficient Network Resource Management
Multi Commander's Network filesystem transforms complex network resource management into an intuitive, integrated experience. The automatic discovery, intelligent caching, and seamless integration capabilities make accessing and managing distributed file resources as natural as working with local files.
Related Network Topics
Explore other virtual filesystem capabilities: Archive Support, Favorites Management, and Virtual Filesystem Overview.